For most of us , Wi - Fi has become our preferred way to plug in our Macs to other networked machine and the Internet . However , most of us also have time when those connections retard down or fail whole . When that happens , however , there are several things you’re able to do to diagnose and ( ideally ) fix the problem .
Signal and noise
The affair to remember about Wi - Fi is that it ’s a strain of radio receiver : signaling are transcend to and from your Mac and your router ( and any other networked equipment ) by transmitter and receivers at both end tuned to the same frequency . While the information being sent might be digital in nature , the medium it rides on is parallel . As such , the power to transfer and receive data via Wi - Fi is dependent on two things : the strength of the signal between those transmitters and receivers ; and the loudness of interference — unusable “ noise”—from other devices using that same relative frequency .
The doctrine of analogy is to listening to the radio in your car : Sometimes , the signaling gets weaker as you drive further off from the station ’s vector . Other sentence , even if the sign is crisp and strong , you might hear two different post — one you want to listen to , one you don’t — on the same channel ; that ’s noise .
Your Mac ’s ability to keep a well Wi - Fi association is a function of both of these signal types : If the signal from your router to your computer is too weak or if there ’s too much racket from competing signals , then — as with your motorcar radio — your Mac will recede its power to make sense of what it ’s “ hearing . ”
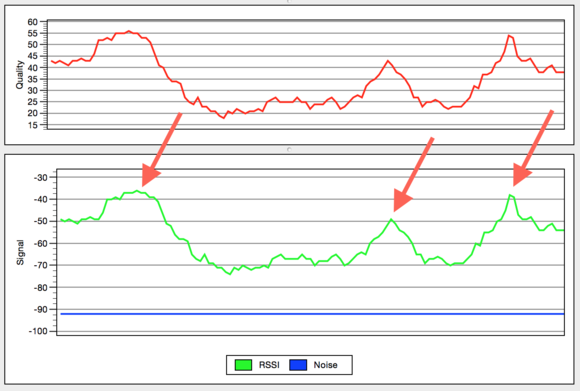
The Wi - Fi signal strength blend up when you are close to the router ( evince by the arrows here ) , and drops off as you move off from it . The noise floor in this example is unremitting , so the signaling - to - noise proportion ( top graph ) just follows the behavior of the signal .
you could see all this natural process in real - time using OS X ’s build - in Wireless Diagnostics service program ( /System / Library / CoreServices / Applications/ ) . Open this utility and choose utility from the Window card . In the venire that then appear , get to the Performance tab . You should see two graphical record : One present the signal and stochasticity levels , another showing the ratio of the two ( a uncouth way to find out proportional intensity ) . ( The levels measured in that first graph are negative because they ’re based on the logarithms of value between 0 and 1 , and such log are damaging . )
In general , for the signaling measurement you want to see values of -10 to -70 dBm ( decibel - milliwatts ) ; for stochasticity , -80 to -100 dBm . As the levels of the signal and of the disturbance get skinny to one another , your wireless connection will start dropping data packets and requiring that they be resent . This will slow down information contagion , and potentially cause your Mac to drop its connecter all in all .
The power of place
If you are having problems with your Wi - Fi connecter , and you ’ve check Wireless Diagnostics , the numbers there ( and the radio analogy above ) should give you some clues about how to limit the problem . One of the most primal things you may do is change the position of your Mac , your router , or both .
Move closer to your routerAs you move your Mac farther from your router , signal military capability will minify . Therefore , try be active closer to your router until you see the sign graph on the Wi - Fi monitor move higher .
Get away from obstructionsLarge metallic element target , window coatings , wires and pipes in walls , and other electrical devices can either block your Wi - Fi signaling and decrease its timber , or introduce noise . Therefore , try go to a new location , away from such obstructions , to see if this meliorate your signaling .
Increase your router ’s radio strengthSome routers have options for changing radio mightiness , which can not only assist increase the timber of the signal your Mac pick up , but also increase your router ’s range . If you have this as a conformation option for your router , then try pose it to its maximum .
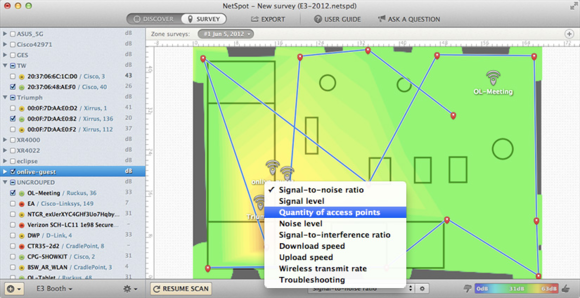
NetSpot ’s power to map signal timbre may aid you determine bushed smear in your office or home .
Draw a mapOne useful coming for valuate misfortunate signal issue is to represent the Wi - Fi quality of your home or business sector . To do this , you may use a plan likeNetSpot , in which you may draw a scurf plan of your edifice , and then move your Mac ( provided it is a laptop computer ) to various locations and graph the measured sign qualities at each one . you may then see if the signals drop off smoothly with the distance from your router ( as you ’d expected ) or if there are any dead spots where signal quality fall off unexpectedly . In doing so , you could see if specific walls or rooms contain hidden buckler that could be obturate the signal , and then be able to posit yourself and others accordingly .
Software and hardware issues
Even if you ’ve done all of the above , you may still have hassle with slow or mixed-up joining . These can be the results of software or ironware problems in your Mac or in your router . diagnose these problems can be daunting , sometimes futile , but you’re able to generally bushel or at least help the office by perform one or more of the following :
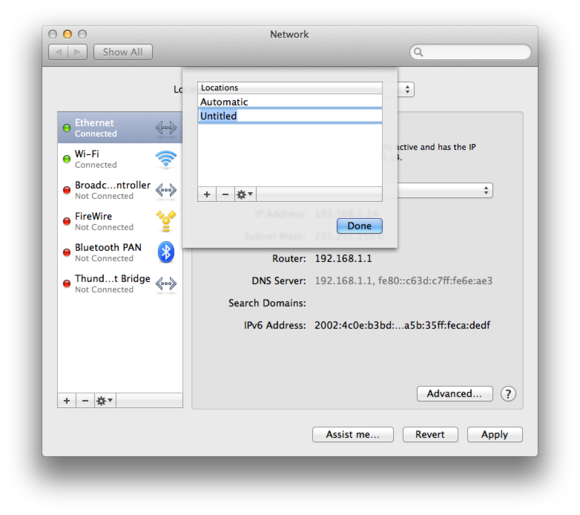
Changing your internet location in this dialog box will bring home the bacon the system with new configurations for your internet port .
prospect are very good that , by the time you get to the conclusion of that listing , you ’ll have fixed whatever problems you might have had . But chances are also very just that , as sentence goes by and your hardware and software system change , as you practice your Mac in new position , Wi - Fi problem will crop up again . But at least you now have a game plan for fixing them when they do .