Full - disc encoding ( FDE ) is a humbled - effort way to ensure that if someone were to get ahold of one of your drive while unmounted or a Mac while power down , the contents on the crusade would be unusable to them without knowing a password or other encryption entropy . Apple offers two decided ways of encrypting volumes on a driving force , and it ’s important to know the difference between them and the current restriction on drive link up to M1 - based Apple Silicon Macs .
FileVault encryption
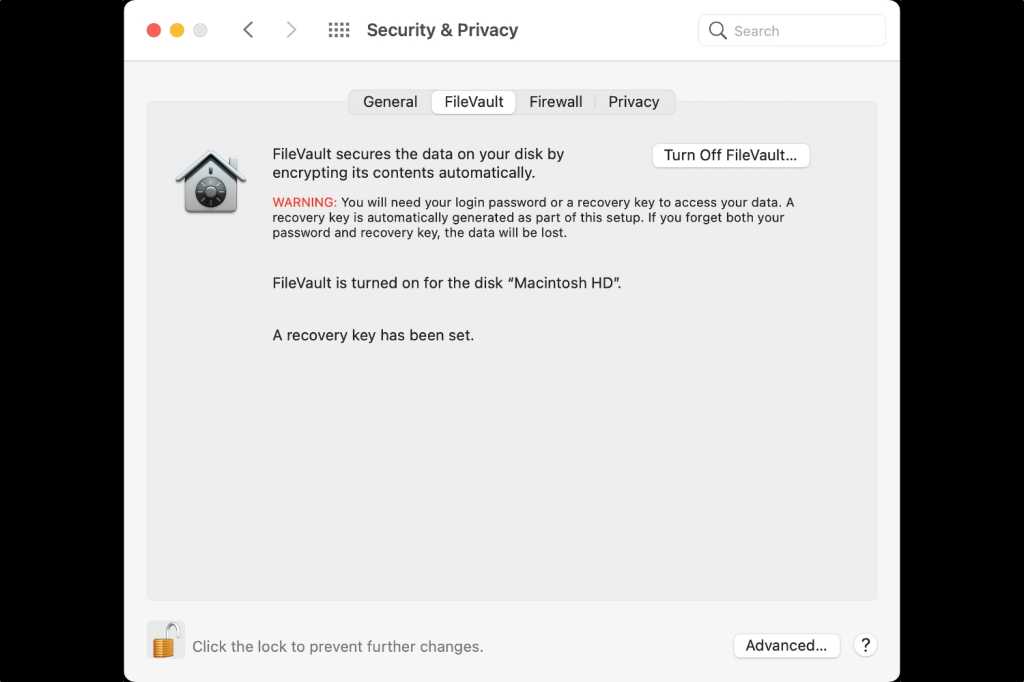
you’re able to readthe full details elsewhere on Macworldabout the in and out of FileVault , but it ’s a fashion to combine the security department of score - establish admission with the assurance of full inscribe information . FileVault is managed via the Security & Privacy preference pane ’s FileVault pane of glass .
How FileVault work out varies based on your role model of Mac :
To turn on FileVault in macOS Big Sur , you actuate it in System Preferences , under Security & Privacy .

Apple
When you enable or disable FileVault protection on a T2 / M1 Mac ’s inner drive , because encoding is always on , FileVault turns on or off forthwith . With an external drive used with an Intel Mac , you may monitor the progress roughly from the FileVault Lucy in the sky with diamonds of the Security & Privacy druthers superman — or see below .
FileVault enables security when powered down for both pre - T2 Macs and T2 / M1 Macs : it forbid admittance at startup without a password for a valid account on the Mac , or for any decrypt datum on the movement if accessed in any style by another Mac or forensic - test equipment .
Drive encryption
Entire volumes can be encrypt directly , but then they can not be used to start up a Mac , because of how FileVault and the startup constituent on Macs interact . encipher such drives is utilitarian when you ’re using them for storage and computer backup .
A cause with volumes code in this mode is to the full available when mounted and the password put down . If you choose to stash away the countersign in the Keychain , then anyone who put on entree to your unlatched Mac and can mount one or more volumes from the movement amplification access as if the contents were n’t cypher .
However , in these cases the encrypted contents are unavailable if no party but you has the watchword to your Mac or the volumes :
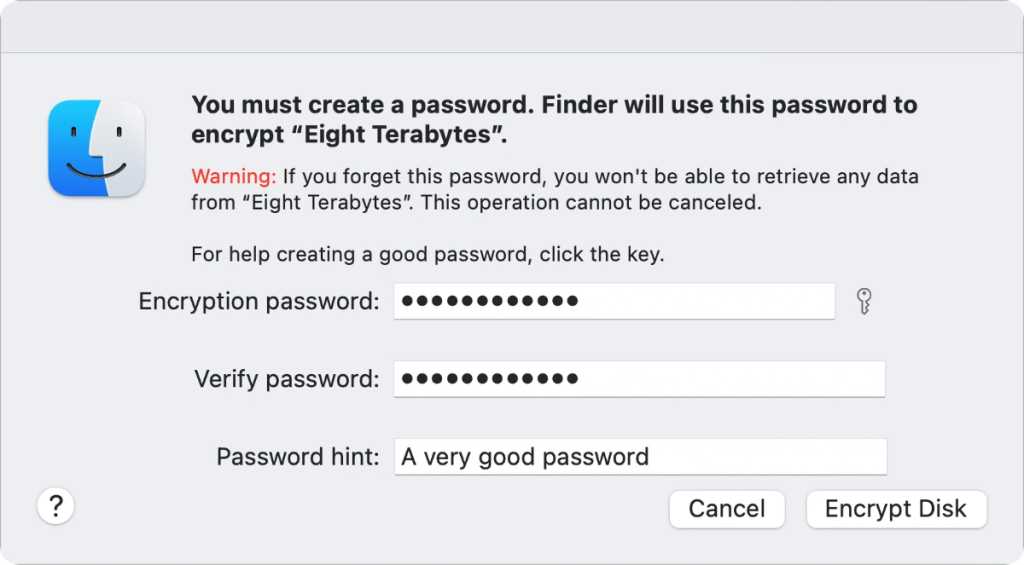
You enable encoding on a campaign very simply from the Finder :
Enter and record the password for your external parkway .
IDG
In Disk Utility , if you essay any bulk that you ’ve encrypted with macOS 10.14 Mojave or subsequently , it shows up with “ Encrypted ” in the excursus for the volume type as “ APFS ( Encrypted ) ” . Disk Utility converts a book that is formatted as Mac OS Extended ( Journaled ) , otherwise have it away as HFS+ , to APFS in the process , and use the APFS ( Encrypted ) subtype .
An of import side note : If you ’re using any volumes on the cause as backup destinations for Time Machine in Mojave or later , immediately from your Mac or over your local web , you do n’t desire to inscribe the drive . Only Macs with Big Sur can backup via Time Machine to an APFS - formatted book . And , in examination , only HFS+ can be used as the data formatting for a destination intensity for networked Time Machine backups , whether the Mac being backed up is running Big Sur or an earlier version of macOS .
you could reverse the mental process by select the drive , choosing Decrypt , come in the word , and then a likewise drawn-out operation occurs to decrypt the drive . If it ’s been commute from HFS+ , it rem
For more advanced user , you may produce cipher volume directly via Disk Utility or the command line , though this involves destructive erasure of volumes , containers , or partitioning , depending on what you ’re trying to batten .
Checking drive encryption status
With an Intel Mac without a T2 silicon chip , with FileVault encrypting an external private road on any Intel Mac , or with any model of Mac encrypting an external non - startup volume , you’re able to monitor progress by using a dictation - line shaft . ( FileVault ’s advance bar is n’t that precise . )
FromApplications > Utilities > Terminal , type the pursuit and closet retort :
diskutil apfs list
This testify all the APFS containers and intensity , and the condition of encoding in progress . You have to scroll through a lot with many disks and volumes to find that information , so you’re able to alternatively type the adopt command to extract just the advancement railway line :
diskutil apfs list | grep Encryption
That will match against tune like :
Encryption Progress : 69.0 % ( Unlocked )
bewilderingly , when encryption is completed , whether it ’s a inauguration volume secured by FileVault or an external volume encrypted via the Finder or other means , thediskutilapp record that encryption is enabled always as :
FileVault : Yes ( unsecured )
Ask Mac 911
We ’ve compiled a list of the doubt we get require most often along with answers and links to columns : take our super FAQ to see if your question is covered . If not , we ’re always count for new problems to solve ! Email yours tomac911@macworld.comincluding screen gaining control as appropriate , and whether you want your full name used . Not every question will be do , we do n’t reply to electronic mail , and we can not allow for direct troubleshooting advice .